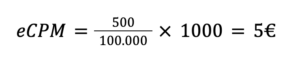What is eCPM in marketing and how is it calculated?
the 15 of August of 2024
the 15/08/2024
In the world of digital advertising, the term eCPM, or Effective Cost Per Thousand Impressions, is essential for evaluating the performance of advertising campaigns. This metric is crucial for both publishers and advertisers, as it helps measure the efficiency of their monetization strategy. In this article, we will explore a detailed guide on eCPM, its importance, the main differences between eCPM and CPM, and how it is calculated.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
What is eCPM?
eCPM, or Effective Cost Per Thousand Impressions, is a metric used in digital marketing to determine the revenue generated for every thousand impressions of an ad. Unlike CPM (Cost Per Thousand), which is a fixed rate advertisers pay for every thousand impressions, eCPM reflects the actual revenue earned from those impressions. This indicator is vital for both publishers, who aim to maximize their advertising revenue, and advertisers, who seek to evaluate the effectiveness of their campaigns.
The importance of eCPM lies in its ability to offer a clear view of an advertising campaign’s performance. For example, if a publisher sells ad space at different rates and models (CPM, CPC, CPA), eCPM allows them to compare the performance of all these models in a unified metric. This way, they can identify which campaigns or ad formats are more profitable.
In practice, eCPM is used to evaluate and optimize advertising campaigns. For example, if an advertiser discovers that a specific campaign has a lower eCPM than expected, they can adjust the ad creative, target audience, or bidding strategy to improve site performance. For publishers, eCPM helps them decide how to allocate their ad inventory to maximize revenue.
How to Calculate eCPM
Calculating eCPM is a straightforward process that involves using a simple formula. The final figure is obtained by dividing Total Revenue by the Number of Impressions and then multiplying by 1,000.
To illustrate how this formula is applied, let’s consider a practical example. Suppose a publisher has generated €500 in revenue from 100,000 ad impressions; the calculation would be as follows:
According to this formula, the publisher earns €5 for every thousand impressions.
Factors Influencing eCPM Calculation
- Inventory Demand: If many advertisers are competing for the same space, the price per thousand impressions is likely to increase.
- Ad Effectiveness: The quality of the ads is essential to maximize performance.
- Audience Targeting: Personalization and precision in targeting play a significant role, positively impacting eCPM.
- Competition: In highly competitive markets, prices may be higher, which increases eCPM.
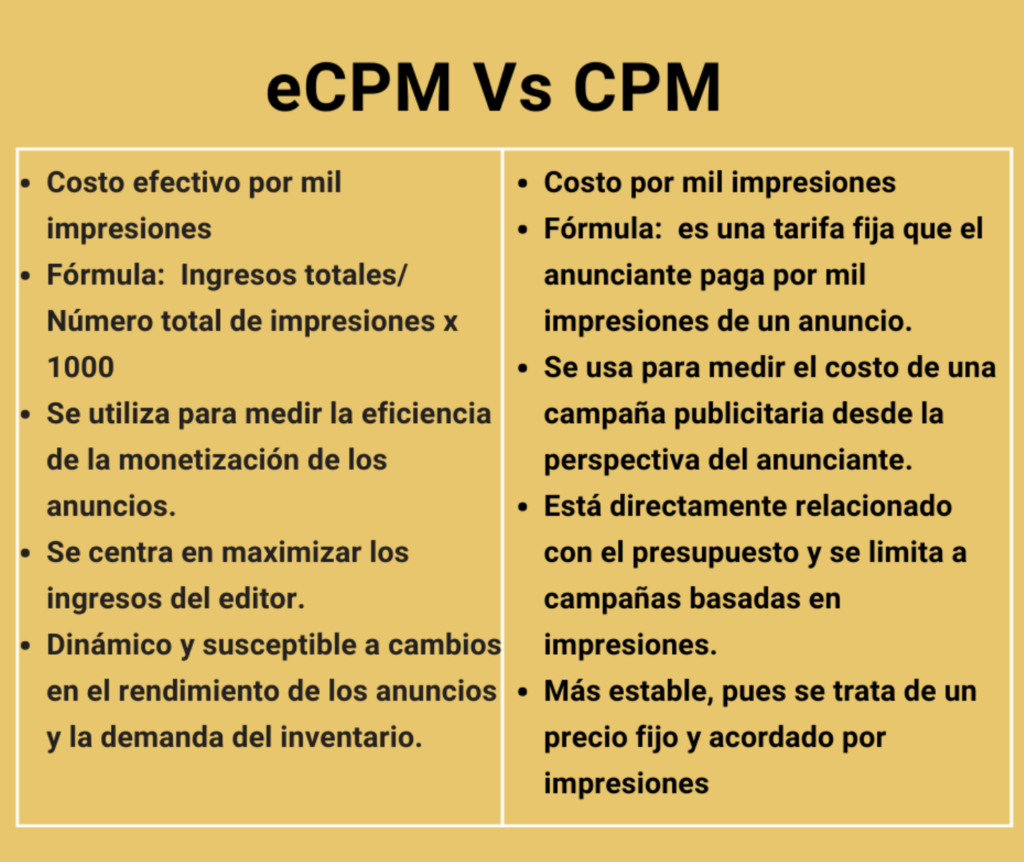
Differences Between eCPM and CPM
Although eCPM and CPM are related terms, there are some key differences between them. Some of these include:
1.- Definition:
eCPM: Represents the Effective Cost Per Thousand Impressions and refers to a metric that indicates how much revenue a publisher generates for every thousand ad impressions, regardless of the pricing model (CPC, CPA, CPM, etc.).
CPM: Stands for Cost Per Thousand Impressions and is the fixed rate an advertiser pays for every thousand ad impressions.
2.- Calculation:
eCPM: Calculated by dividing total revenue by the total number of impressions and multiplying by 1,000.
CPM: A fixed pre-established rate that the advertiser pays for every thousand ad impressions, without considering the revenue earned.
3.- Perspective:
eCPM: Used to measure the efficiency of ad monetization. It is a useful indicator for publishers who want to optimize their total revenue from various advertising sources.
CPM: Used to measure the cost of an advertising campaign from the advertiser’s perspective, determining how much to pay for every thousand impressions at a fixed price. It is useful for planning and budgeting ad campaigns based on ad visibility.
4.- Revenue:
eCPM: Focuses on maximizing the publisher’s revenue by considering all forms of monetization and providing a common metric to evaluate overall effectiveness.
CPM: Directly related to the advertiser’s budget and is limited to impression-based campaigns. The publisher’s revenue depends on the volume of impressions and the agreed-upon CPM rate.
5.- Variability:
eCPM: Can vary significantly because it includes different types of revenue, making it more dynamic and susceptible to changes in ad performance and inventory demand.
CPM: Generally more stable, as it is a fixed price agreed upon per impression. It may vary if different rates are negotiated for different campaigns or periods in the advertising contract.
Understanding eCPM is crucial for optimizing revenue and evaluating the effectiveness of advertising campaigns. This metric not only helps publishers identify the best monetization opportunities but also assists advertisers in adjusting their strategies to maximize return on investment. In a competitive digital environment, eCPM provides a clear and accurate view of ad performance, enabling all parties involved to make informed and strategic decisions.